Effective revenue cycle management (RCM) is crucial for healthcare organizations striving to optimize cash flow, reduce denials, and improve patient financial experiences. Understanding the full spectrum of RCM—from initial patient engagement to post-payment analysis—can significantly impact operational efficiency and financial health. This guide delves into the five primary stages of RCM, details the 16 critical […]
Effective revenue cycle management (RCM) is crucial for healthcare organizations striving to optimize cash flow, reduce denials, and improve patient financial experiences. Understanding the full spectrum of RCM—from initial patient engagement to post-payment analysis—can significantly impact operational efficiency and financial health. This guide delves into the five primary stages of RCM, details the 16 critical […]
Effective revenue cycle management (RCM) is crucial for healthcare organizations striving to optimize cash flow, reduce denials, and improve patient financial experiences. Understanding the full spectrum of RCM—from initial patient engagement to post-payment analysis—can significantly impact operational efficiency and financial health. This guide delves into the five primary stages of RCM, details the 16 critical steps involved, and offers expert insights on responsibility, outsourcing, and process improvement strategies to ensure your organization maximizes revenue while maintaining high standards of care.
Healthcare providers that embrace a structured approach to revenue cycle management can better navigate the complexities of insurance claims, coding, billing, and collections. Moreover, integrating innovative technologies like artificial intelligence and virtual reality in medicine can further streamline operations and enhance patient outcomes. For example, advanced tools for virtual reality in medicine are transforming diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, leading to more accurate billing and treatment plans.
In this context, organizations must also stay informed about cutting-edge developments such as VR and AR applications in healthcare, which are revolutionizing patient engagement and provider training. Additionally, leveraging artificial intelligence in healthcare enables predictive analytics that can optimize revenue cycles and reduce administrative burdens.
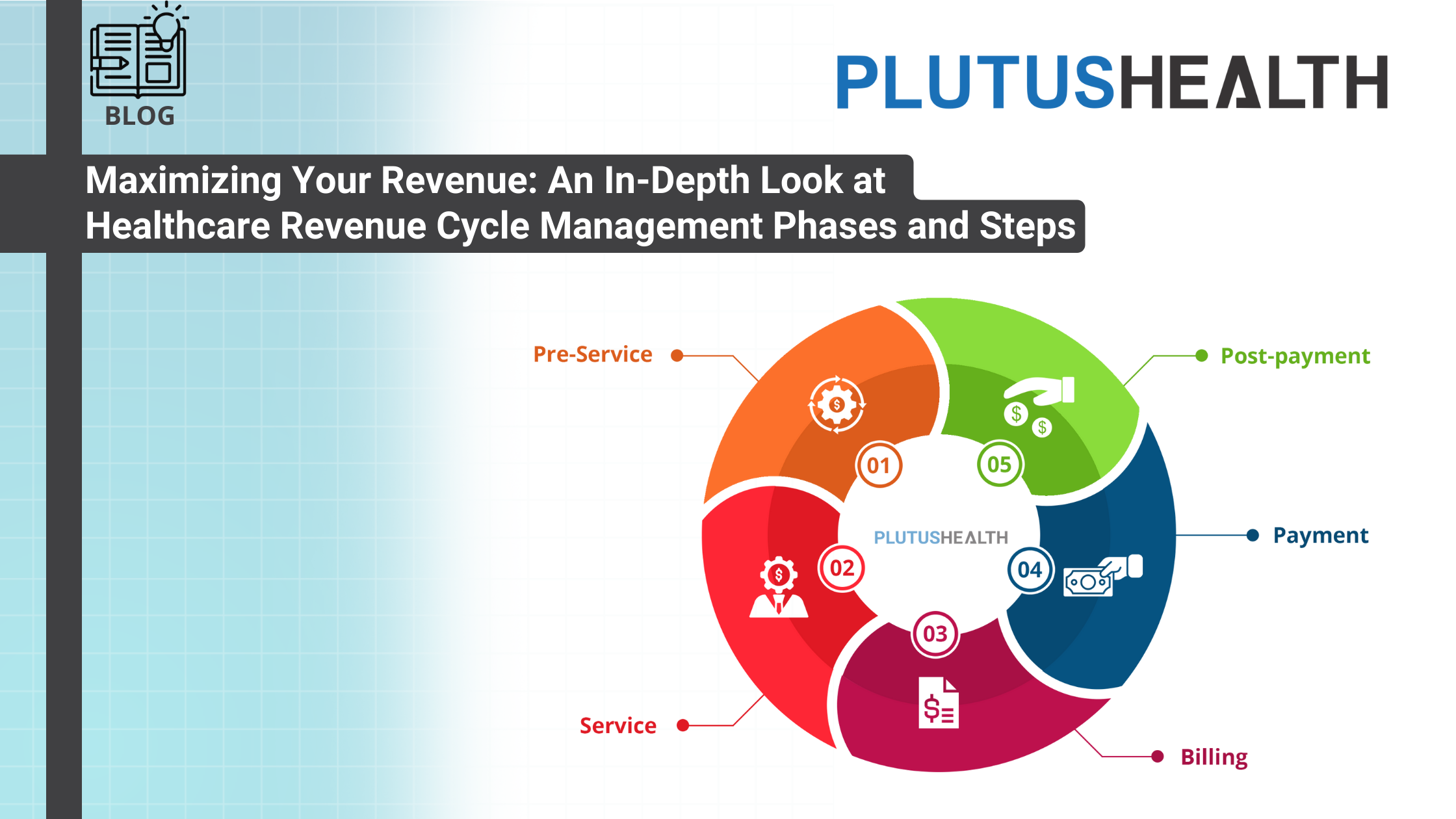
Revenue Cycle Management Stages
The journey of revenue cycle management in healthcare encompasses five essential stages, beginning with pre-service preparations and culminating in detailed post-payment analysis. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that providers receive appropriate reimbursement for their services, while also maintaining compliance and delivering quality patient care.
- Pre-service: This initial phase occurs before the patient sees the healthcare provider. It involves verifying insurance coverage, confirming provider-payer contract details, and scheduling appointments. Accurate patient registration is critical here, including thorough collection of demographic and insurance information, which helps prevent denials rooted in data errors.
- Service: During the patient encounter, providers document the visit, assign appropriate procedure codes (CPT) and diagnosis codes (ICD), and record the services rendered. Precise clinical documentation and coding are foundational for proper billing and reimbursement.
- Billing: After services are provided, the healthcare organization generates detailed bills and submits claims electronically to payers such as Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurers. Ensuring that claims are complete and accurate reduces the risk of rejections. In many cases, secondary insurance coverage must also be billed, adding another layer of complexity.
- Payment: This phase involves collecting payments from payers and patients. It includes tracking incoming payments, managing delayed or partial payments, and following up on outstanding balances. Effective payment posting and reconciliation are essential to maintaining an accurate accounts receivable status.
- Post-payment: The final stage involves analyzing billing cycle metrics, including days in accounts receivable, collection rates, and billing accuracy. Continuous monitoring allows organizations to identify bottlenecks, improve processes, and ensure full reimbursement.
The 16 Critical Steps in Revenue Cycle Management
To execute a seamless RCM process, organizations must implement the following steps systematically. These steps span from pre-service verification to post-payment evaluation:
1. Verify Provider Credentials: Ensure all healthcare providers possess valid licenses and credentials. Automated tools can facilitate this verification, which should occur immediately upon hiring to prevent claim denials related to credentialing issues.
2. Verify Provider Contract with Insurers: Confirm that the provider has signed and up-to-date contracts with insurance payers. Updating payer agreements in the billing system helps identify underpayments and denials early.
3. Patient Registration: Collect comprehensive patient details, including insurance information and medical history, prior to service delivery. Accurate data entry at this stage minimizes billing errors and claim rejections.
4. Scheduling: Arrange appointments with precise date and time records, especially for services requiring detailed billing like mental health or behavioral therapies, where appointment duration impacts reimbursement.
5. Eligibility and Benefits Verification: Confirm patient insurance coverage and benefits just before the appointment to avoid coverage lapses. Real-time verification reduces claim denials due to coverage issues.
6. Prior Authorization: Obtain pre-approval from insurance carriers for services that require prior authorization, such as surgeries or specialized treatments. This step prevents claim rejections stemming from missing approvals.
7. Medical Coding: Assign accurate CPT and ICD codes to services and diagnoses. Proper coding ensures compliant billing and maximizes reimbursement potential.
8. Charge Entry and Capture: Record the services and their associated charges accurately in the billing system, aligning with established fee schedules. Review processes help detect discrepancies before claim submission.
9. Claim Submission: Submit claims electronically via EDI to payers, ensuring completeness and correctness. Prompt submission and follow-up on rejections are vital for maintaining cash flow.
10. Denial Management: Analyze rejected claims to understand payer reasons. Correct errors, provide additional documentation, and resubmit claims promptly to recover potential revenue.
11. Insurance Follow-up: Monitor outstanding claims, provide supplementary information as needed, and expedite resolution of unpaid or denied claims to minimize AR days.
12. Patient Billing: After insurance payments, bill patients for remaining balances promptly. Clear, timely statements improve collection rates and patient satisfaction.
13. Patient Collections: Implement strategies like online payments and reminders to enhance collection efficiency. Tracking patient receivables is critical for revenue integrity.
14. Payment Posting: Record payments from payers and patients immediately, reconciling with outstanding balances. Automated posting reduces errors and provides an accurate financial picture.
15. Reporting: Utilize RCM software to generate key performance indicators (KPIs), such as collection rates and days in AR, for ongoing process improvement.
16. Financial Evaluation: Analyze collected data to identify inefficiencies and optimize workflows. Experts suggest outsourcing this step if internal resources lack the necessary expertise, ensuring continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Communication and Quality Control
Effective communication and rigorous quality control are the backbone of a high-performing RCM process. Clear channels between front-office and back-office teams prevent data discrepancies that could lead to claim denials. Regular audits by quality control teams help detect process gaps, ensuring compliance and accuracy across all steps.
As organizations grow, leveraging tools like dashboards can provide real-time insights into revenue cycle performance. Outsourcing certain steps, such as collections or denial management, can free internal resources for patient care and strategic initiatives. For instance, virtual reality in medicine is transforming provider training and patient engagement, complementing efforts to streamline revenue management.
Responsibility for RCM Tasks: Internal vs. Outsourced
While many healthcare organizations perform initial steps such as patient registration and scheduling internally, they often outsource post-service processes like claim submission, denial management, and collections. Small practices tend to handle coding and billing internally, whereas larger hospitals usually delegate these functions to specialized RCM service providers.
Outsourcing most revenue cycle steps can lead to increased efficiency and improved cash flow. For example, external agencies are usually better equipped to handle complex claim follow-ups and appeals, which are resource-intensive tasks. As Ron Walton emphasizes, understanding every aspect of the revenue cycle through dashboards is essential, whether performed internally or outsourced.
Conclusion
Optimizing revenue cycle management requires a comprehensive understanding of each phase, meticulous execution of all steps, and continuous process evaluation. Embracing technological advancements, fostering clear communication, and strategically outsourcing non-core activities can significantly improve financial performance and patient satisfaction. By aligning operations with industry best practices and leveraging innovative solutions, healthcare providers can ensure sustainable growth and high-quality care delivery in the evolving landscape of modern medicine.